The fall of Bashar al-Assad's regime: Who now controls which areas in Syria?
Visual JournalismAhda, BBC NewsDecember,11,2024.
Pros and Cons of the Fall of Bashar al-Assad's Regime
Pros:
1. End of Authoritarian Rule:
The fall could mark an end to decades of autocratic governance, allowing for potential democratic reforms.
2. Increased Autonomy for Regions:
Kurdish and other regional forces might gain autonomy, ensuring better representation of diverse groups.
3. New Alliances and Stability:
With Assad gone, international stakeholders might work more cohesively to stabilize the region.
4. Economic Reconstruction:
A new government may attract global investments for rebuilding war-torn areas.
Cons:
1. Power Vacuum:
The absence of a strong central authority could lead to infighting and further fragmentation.
2. Rise of Extremism:
Terrorist organizations may exploit the instability to expand their influence.
3. Humanitarian Crisis:
Continued displacement and civilian casualties might worsen due to prolonged conflicts among factions.
4. Geopolitical Proxy Wars:
Competing interests of global powers (e.g., Russia, the U.S., Turkey) could escalate regional tensions.
In just two weeks, Syrian rebels have seized several major cities in the northwest of the country and advanced to the capital, Damascus, where they have ended Bashar al-Assad's 24-year rule.
In convoys of small cars and motorbikes, the rebel group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham advanced rapidly along a north-south highway and captured Damascus without much resistance.
While many are celebrating the ouster of Syria's ruling family, the future remains uncertain and the situation in Syria is changing by the minute as different rebel groups take control of different parts of the country.
Who controls which areas in Syria?
The fall of Bashar al-Assad's government was brought about by a sudden and unexpected advance by Hayat Tahrir al-Sham rebels, but while the group controls major cities in Syria, it does not rule the entire country.
Parts of Syria have been controlled by various rebel groups for years, including Hayat Tahrir al-Sham in Aleppo and Kurdish forces in the northeast.
Rebel groups have also seized more territory in the past few days and weeks.
It is clear that no rebel group will regret the fall of Bashar al-Assad's government, but how to run the country could prove difficult in the coming days, and there have already been reports of clashes between rival groups in the north of the country.
How did the rebels get to Damascus?
The rebels, who had been in the icy north for years, advanced with lightning speed to overthrow the president and seize the capital over the weekend.
After completely capturing Syria’s second city, Aleppo, in November, the rebels continued their advance and captured the key city of Hama in the south on Thursday.
The advance was lightning fast, and Homs, Syria’s third city, was quickly captured on Saturday.
The rebels also easily captured the capital, Damascus, the next day.
Where is Syria and what kind of interference is it from its neighbors?
Syria has a population of 22 million and is located east of the Mediterranean Sea. It borders Turkey to the north, Lebanon and Israel to the west and southwest, Iraq to the east, and Jordan to the south.
During the Syrian conflict, Turkey, Western powers, and several Gulf states have supported various groups of Syrian opposition groups in various ways.
Hezbollah in Lebanon, which is backed by Iran, has fought against government forces in Syria in the past but has been weakened by the recent conflict with Israel.
Experts say this is a key reason why the rebels have advanced so rapidly.
Israel has long described Syria as Iran’s “defensive front” and has carried out airstrikes there since the fall of Bashar al-Assad’s government.
How did Israel respond?
Israeli warplanes have reportedly carried out hundreds of strikes in various areas of Syria, including Syrian military bases, weapons warehouses, ammunition depots, airports, naval bases and research centers.
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, a Britain-based monitoring group, says it has collected data on 300 Israeli strikes so far, including attacks on Damascus, Aleppo and Hama.
Most of the targets were reportedly completely destroyed.
Israel says its operations are aimed at preventing the weapons from falling into the hands of “extremists.”
Israel also says it has taken control of a buffer zone on the Golan Heights, and that a 1974 agreement with Syria ended after the fall of Bashar al-Assad's government.
It has denied reports that its tanks have reached Damascus, but has said that some military units are in Syrian territory beyond the buffer zone.
The Golan Heights are a 60-kilometer-long rocky area located 60 kilometers southwest of Damascus.
Israel captured the territory from Syria at the end of the 1967 Six-Day War and unilaterally annexed it in 1981.
Israel's move was not recognized internationally, but was recognized by the United States in 2019.
What is happening in northern Syria?
Clashes have broken out between Turkish-backed rebels and Kurdish forces in the northern Syrian city of Manbij.
Both sides claimed to have captured parts of the city, and clashes are still ongoing in some areas.
Some experts at the Institute for the Study of War say they do not know who controls Manbij.
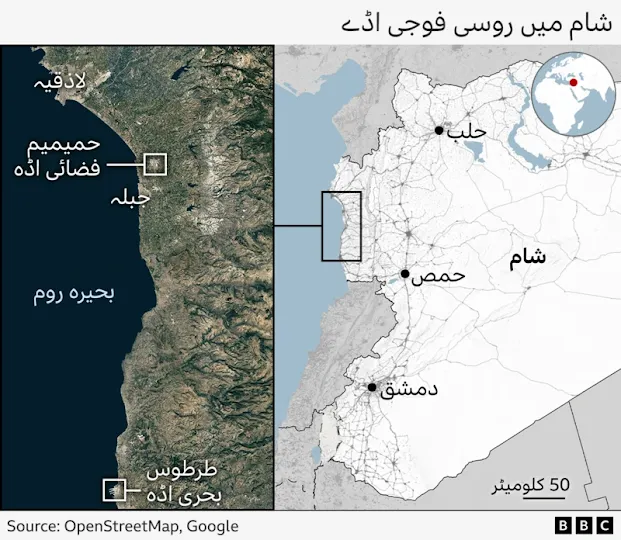
Where are the Russian military bases in Syria?
In 2015, Russia sent thousands of troops to Syria to keep President Bashar al-Assad in power.
In exchange for this military assistance, Russia was granted a 49-year lease on two key military bases.
The port of Tartus is Russia's only naval base abroad and in the Mediterranean.
The Hmeimim air base is used by Russia to transport its contractors to and from Africa. Both bases enable Russia to play its role as a global power.
The Kremlin says it will discuss the future of both bases with the new Syrian administration.
Related Topics
#Syria #Middle_East














No comments: